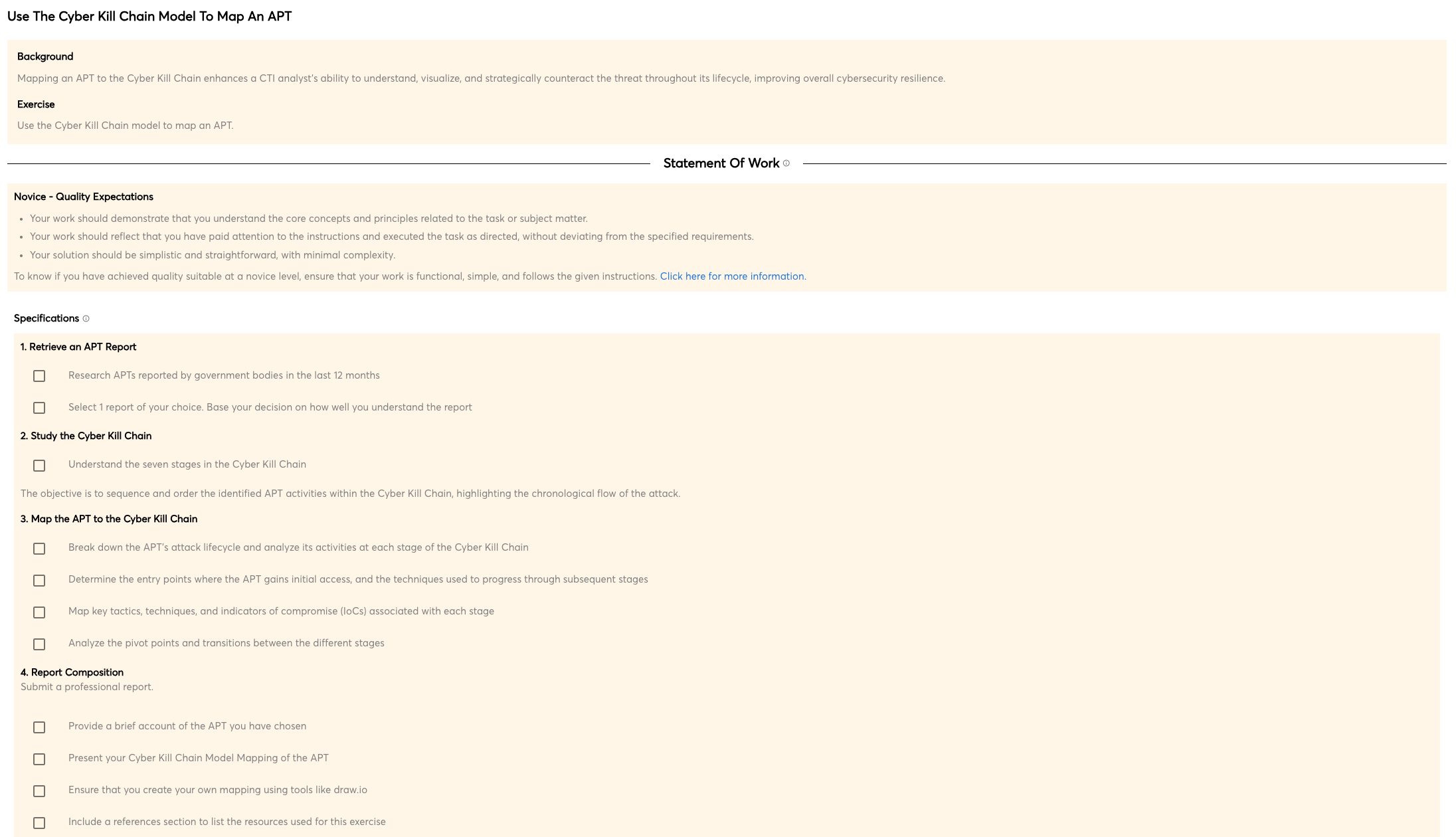
There is no one-size-fits-all answer when it comes to offensive countermeasures operations, such as hacking back. Depending on the specific situation and threat, a variety of tactics and techniques may be necessary to successfully achieve the desired outcome. However, some basics that are generally applicable include reconnaissance and mapping of the target environment, identification of potential entry points and vulnerabilities, as well as deployment of appropriate tools and techniques to exploit those vulnerabilities.
Once the attack is launched, it is important to maintain consistent monitoring and analysis of the target environment to ensure that the threat is neutralized and that no further damage is done. In some cases, it may also be necessary to take further defensive measures to protect the organization's systems and data.
The bottom line is that effective offensive countermeasures require a high level of sophistication and expertise, and should be undertaken only after a careful risk analysis has been conducted.
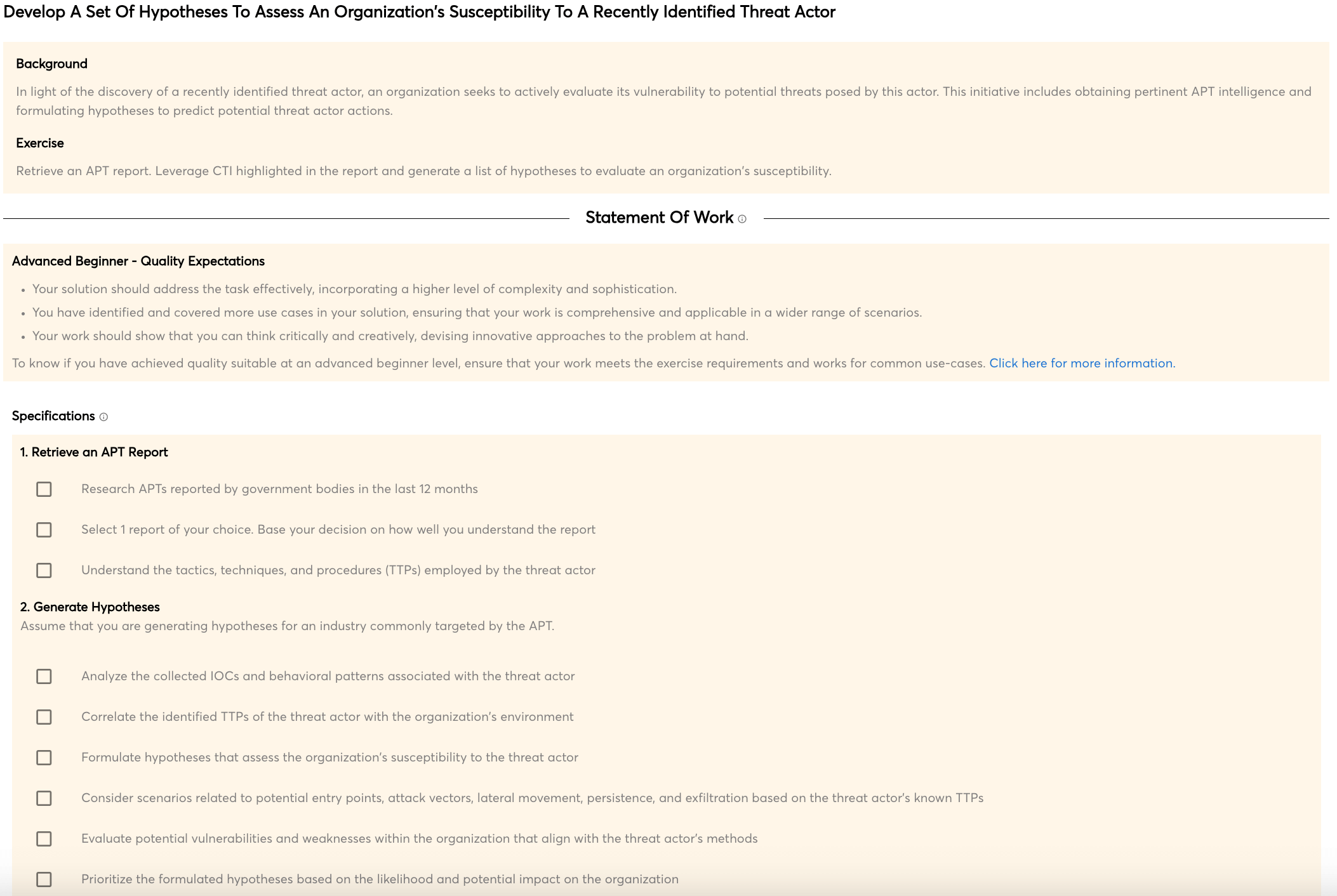
Safely probing adversary infrastructure
One of the main goals of any cyber offensive countermeasure (COCM) is to safely probe adversary infrastructure in order to understand their activity, identify any valuable assets, and understand their attack surface. It is also important to identify any potential vulnerabilities that could be exploited in order to achieve this goal. This course teaches techniques to perform scans in way that cannot be attributed back to a OCM team.
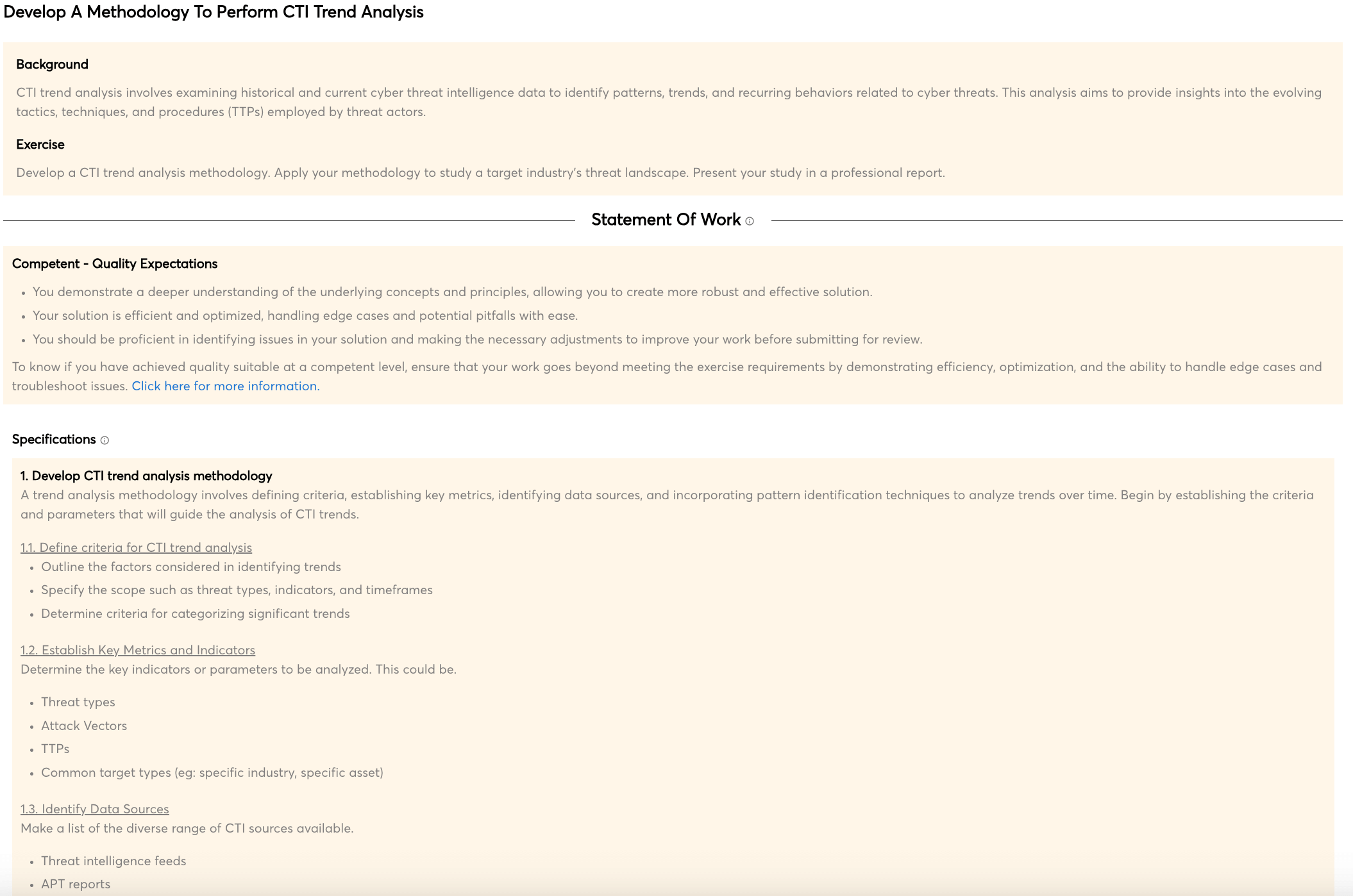
Identifying vulnerabilities in control panels
Cyber threat actors write malware with the goal of establishing a foothold in the target environment. Once they have achieved this, they need to be able to control the malware in order to achieve their goals. This is where malware control panels come into play. These panels provide a web-based interface that allows the attacker to control the malware, issue commands, and gather information.
However, these panels can also be hacked by offensive countermeasures teams. This allows the team to take over the malware, stop it from doing damage, and even use it to track down the attacker.
Building and using a secure operating environment
Building and using a secure operating environment is crucial in developing reliable cyber offensive countermeasures. Without a stable and secure system, any actions taken against potential cyber threats could be easily compromised, rendering the entire effort useless.
Building and deploying honeypots
A honeypot is a computer system that is configured to act as a decoy to lure cyber attackers. Once the attacker is attracted to the honeypot, their activities can be monitored and analyzed. This information can then be used to improve the security of the organization's real systems.
Building and deploying honeypots is an important part of cyber offensive countermeasures. By setting up honeypots, we can learn about the tactics and techniques used by attackers, as well as the tools and malware they use.

 Intermediate
Intermediate